Introduction
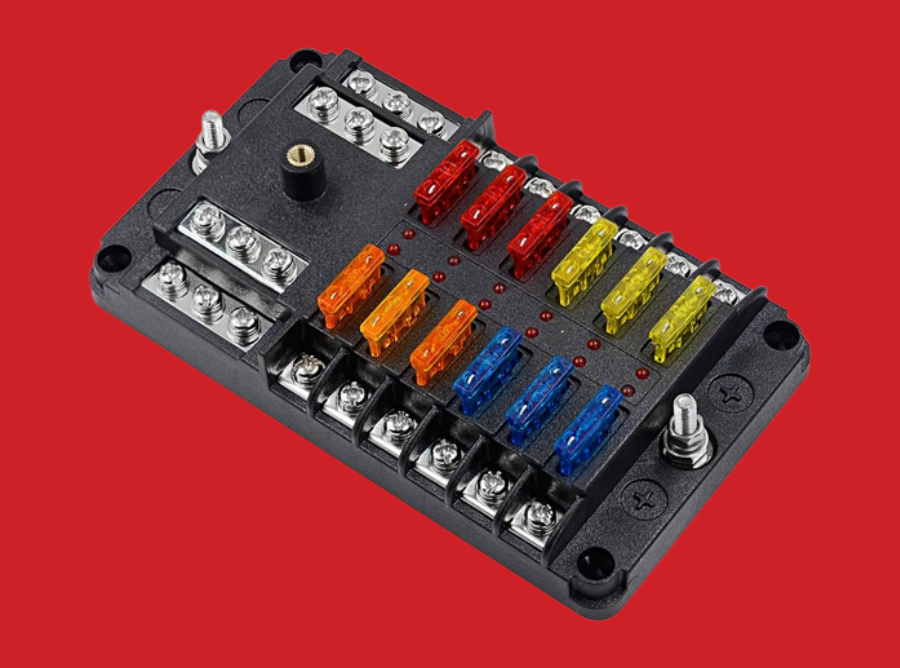
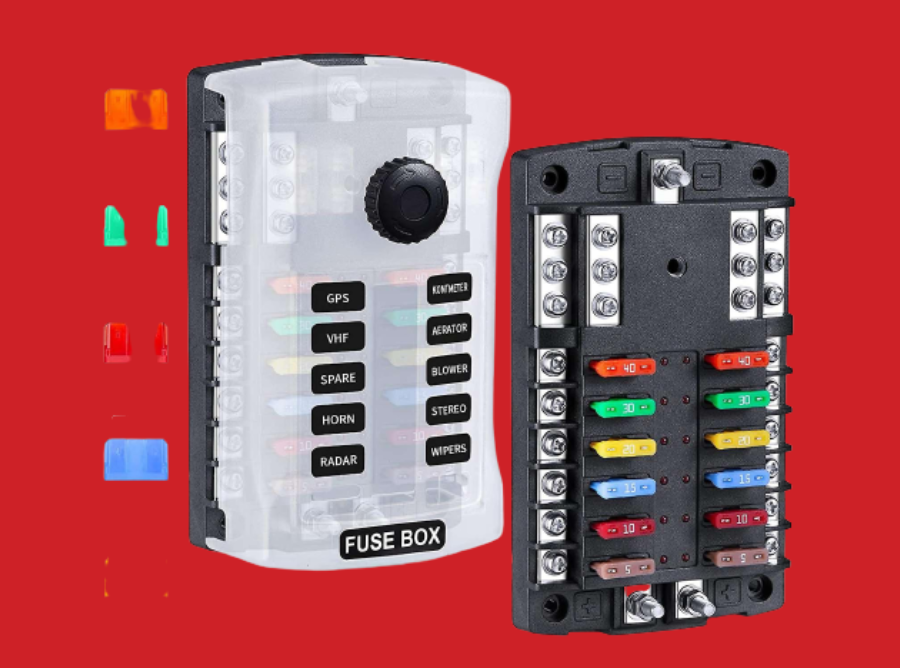
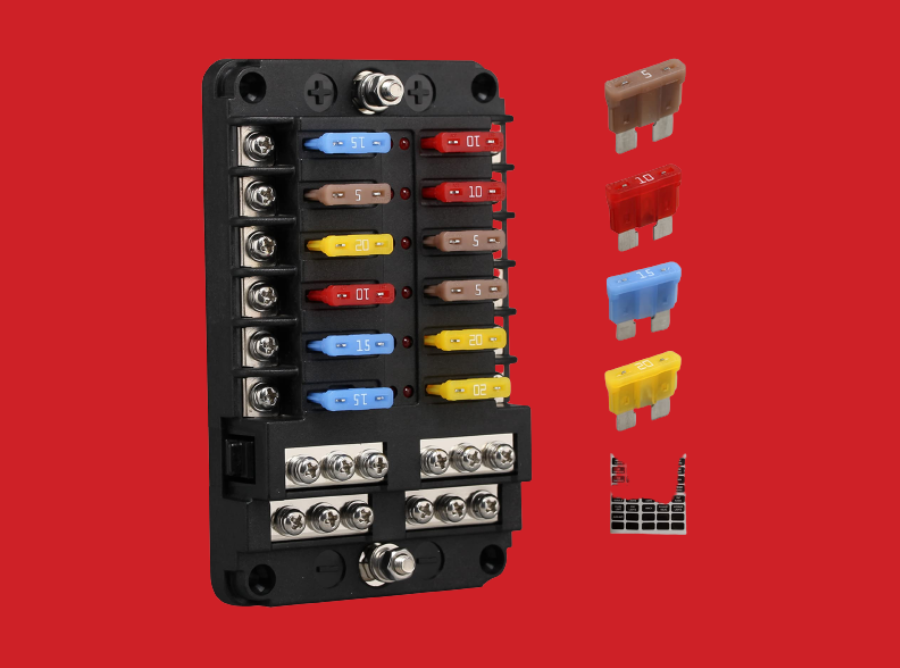
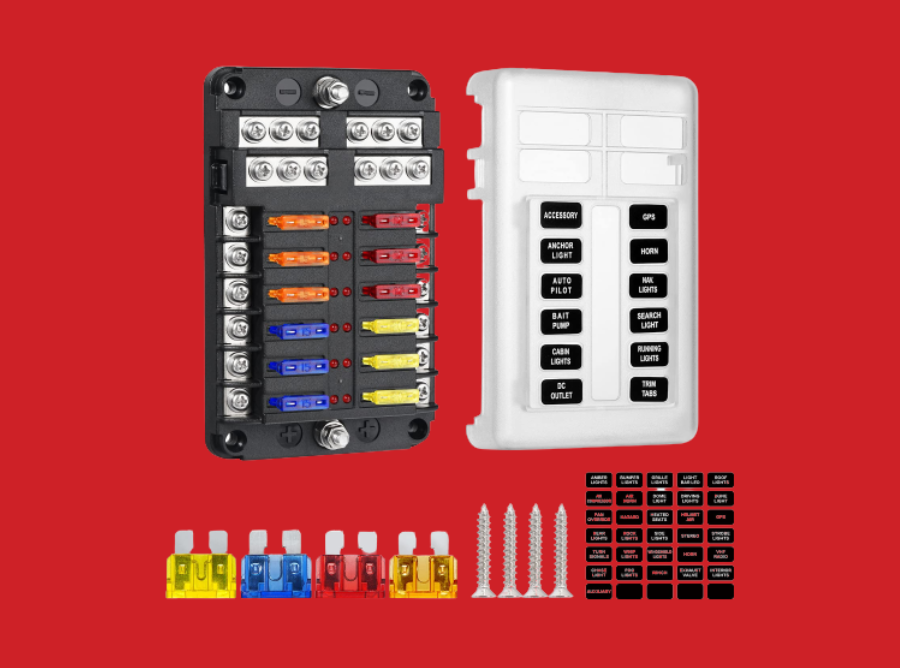
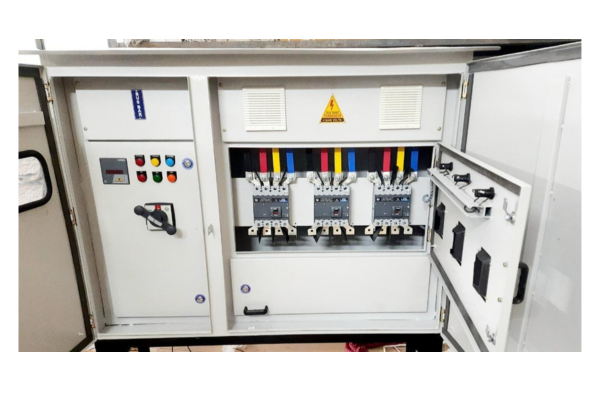
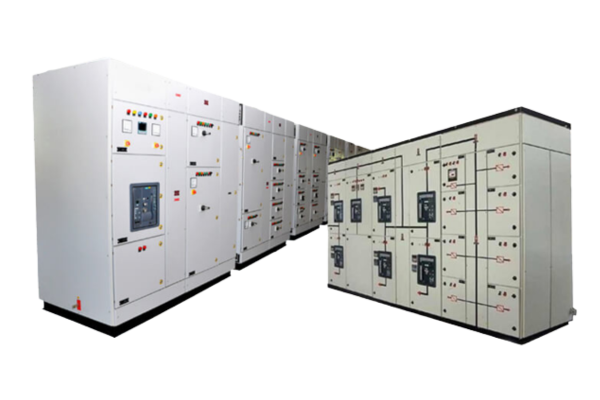
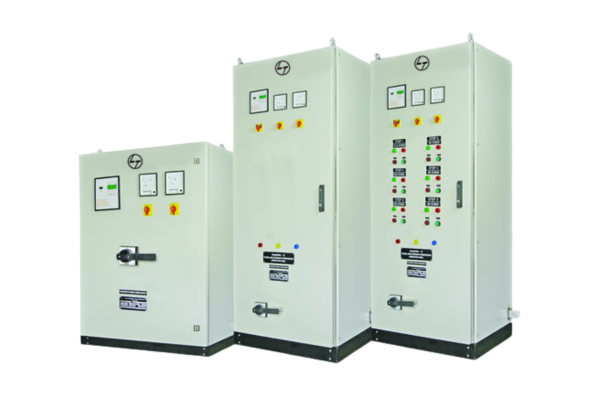
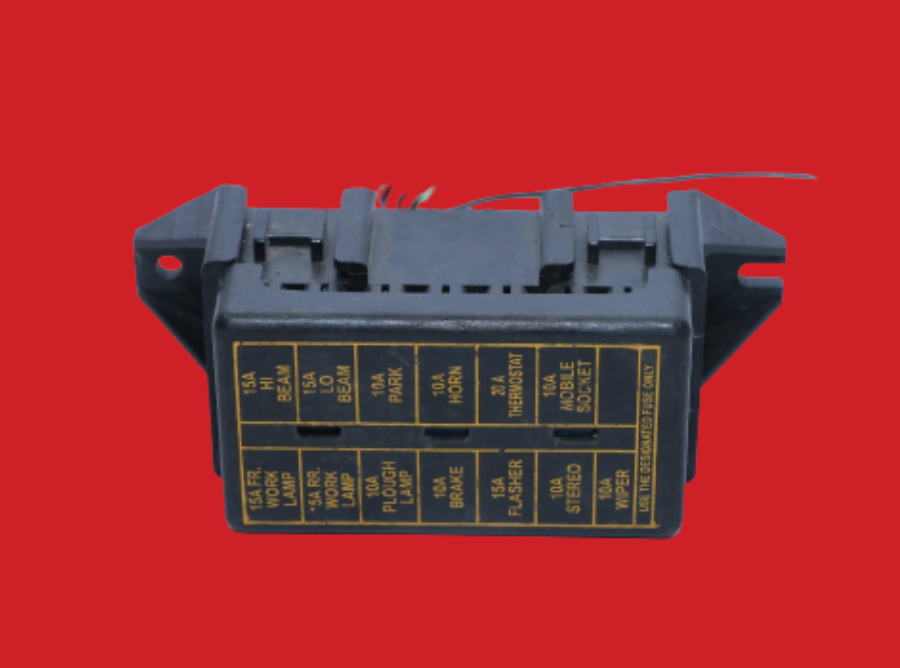
A fuse box, also referred to as a consumer unit or distribution board, is a crucial component in electrical systems that provides protection to circuits and electrical devices within a building. Fuse boxes house fuses or circuit breakers that act as safety devices to prevent overcurrent, short circuits, and other electrical faults that could pose hazards to both people and property. In this article, we will explore the functions, components, types, and benefits of fuse boxes.